Snake River

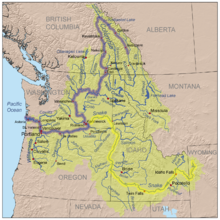
Rugged mountains divided by rolling plains characterize the physiographically diverse watershed of the Snake River. The Snake River Plain was created by a volcanic
hotspot which now lies underneath
Yellowstone National Park, the headwaters of the Snake River. Gigantic glacial-retreat flooding episodes that occurred during the previous
Ice Age carved out many topographical features including various canyons and ridges along the middle and lower Snake. Two of these catastrophic flooding events significantly affected the river and its surrounds.
More than 11,000 years ago, prehistoric
Native Americans lived along the Snake.
Salmon from the Pacific Ocean spawned in the millions in the river. These fish were central to the lives of the people along the Snake below
Shoshone Falls. By the time
Lewis and Clark crossed the Rockies and sighted the valley of a Snake tributary, the
Nez Perce and
Shoshone were the most powerful people in the region. Contact with Europeans introduced horses to some tribes, reshaping their lifestyles for the next few hundred years before outside settlement. Later explorers and fur trappers further changed and used the resources of the Snake River basin. At one point, a hand sign made by the Shoshones representing fish was misinterpreted to represent a snake, giving the Snake River its name.
By the middle 19th century, the
Oregon Trail, a pioneer trail of which a major portion followed the Snake River, had been established.
Steamboats and railroads moved agricultural products and minerals along the river throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries. The powerful, steep flow of the Snake River has been utilized since the 1890s to generate
hydroelectricity, enhance navigation and provide irrigation water from fifteen major dams that have transformed the lower river into a series of
reservoirs, several of which have been proposed for removal to restore some of the river's once-tremendous salmon runs.
Brought to you by: http://coffeeganoderm.blogspot.com
From: wikipedia.org


